1.Masalah jaringan karena kegagalan piranti jaringan
Skala gangguan akibat dari kegagalan piranti jaringan juga bisa bervariasi, dari hanya sebuah komputer karena kegagalan NIC – lan card; beberapa komputer karena kegagalan switch; atau bahkan berskala luas karena kegagalan pada switch central yang menghubungkan jaringan server. Untuk kegagalan lan card di salah satu komputer bisa diganti dengan network card cadangan anda.
Terus bagaimana kalau kegagalan jaringan itu akibat kerusakan pada switch? Design anda mengenai redundansi jaringan akan sangat membantu dalam menyelamatkan kegagalan jaringan anda. Kebutuhan load balancing dan redundansi haruslah dikaji untuk setiap kebutuhan berdasarkan penggunaan link redundansi; piranti router; switch dan multi-homed host yang bersifat kritis. Tujuan dari system redundansi ini dimaksudkan untuk menjamin ketersediaan layanan dimana tidak ada satupun titik rawan kegagalan.
2.Hal yang perlu di upgrade yaitu Masalah jaringan karena kegagalan kabel jaringan
Yang ini merupakan masalah jaringan yang umum kita temui akibat putusnya kabel jaringan yang bisa mempengaruhi kinerja sebuah komputer dalam jaringan karena putusnya kabel patch anda karena digigit tikus; masalah jaringan yang berdampak pada satu blok gedung karena putusnya kabel antar switch (uplink cable); atau bahkan berdampak pada sebagian besar komputer dalam jaringan lan anda karena kegagalan backbone cable.
3.anti virus perlu diupgrade untuk memperlancar jaringan
Jumat, 31 Desember 2010
Kamis, 09 Desember 2010
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 9 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1.

Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output shown, to which IP network should the workstations in the Support department belong?
• 192.168.1.0
• 172.16.1.0
• 172.16.3.0
• 172.16.5.0
2.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is doing proactive network maintenance. The administrator pings 192.168.1.100 and compares the results to the baseline data. Based on the comparison of the two pings, what is one possibility?
• There is an ACL applied, making the destination host unreachable.
• There is a malfunctioning NIC on the destination host.
• The sending host is unable to access the network.
• There are congestion problems on the network.
3.

Refer to the exhibit. Given the output generated by the debug ppp negotiation command, which statement is true?
• The line protocol of the local router is now up.
• The username ’Goleta’ is configured locally.
• The command ppp authentication pap is configured on both routers.
• The local router requested to terminate the session.
4. What is important to consider while configuring the subinterfaces of a router when implementing inter-VLAN routing?
• The subinterface numbers must match the VLAN ID number.
• The physical interface must have an IP address configured.
• The IP address of each subinterface must be the default gateway address for each VLAN subnet.
• The no shutdown command must be given on each subinterface.
5.

Refer to the exhibit. A lab technician connects two routers together via a serial cable using the default interface configuration values. The interfaces are up; however, the technician is unable to ping between the two devices. What is the most likely problem?
• The lab technician used the wrong cable to connect the serial ports.
• There is an IP mismatch between the serial ports.
• There is an encapsulation mismatch between the serial ports.
• No clock rate has been set on the DCE interface.
6.

Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output shown, why is VTP information unable to propagate the network?
• One of the two client mode switches must be reconfigured to Transparent mode.
• Each switch must be synchronized to the network time server.
• The VTP domain names are different.
• VTP passwords must be set.
• The configuration revision numbers are all the same.
7. The enterprise mail server software recently went through a minor update. A network administrator notices an excessive amount of traffic between a database server and the newly updated mail server, compared to the baseline data. What is the first action the administrator should do to investigate the problem?
• Wait to see if the recent update will stabilize after a while.
• Redo the baseline data to include the minor upgrade.
• Check the log to see what software components are producing the excess traffic.
• Check for viruses and spyware on the database server.
8.

Refer to the exhibit. Users are reporting that they cannot access the Internet. Routers R1 and R2 are configured with RIP version 2 as shown. If R2 receives a packet with a destination address on the Internet, how is the packet routed?
• The packet is routed to the ISP router and then to network 10.1.1.0/24.
• The packet is routed to the ISP router and then to the Internet.
• The packet is routed to R1 and then forwarded out Fa0/0 on R1.
• The packet will not be routed because R2 does not have a valid default route.
9.

Refer to the exhibit. Both routers are configured using RIPv1. Both routers are sending updates about the directly connected routes. R1 can successfully ping the serial interface of R2. The routing table on R1 does not contain any dynamically learned routes from R2, and the routing table on R2 shows no dynamically learned routes from R1. What is the problem?
• Subnetting is not supported by RIPv1.
• One of the routers needs a clock rate on the serial interface.
• The serial link between the two routers is unstable.
• VLSM is not supported by RIPv1.
10.
R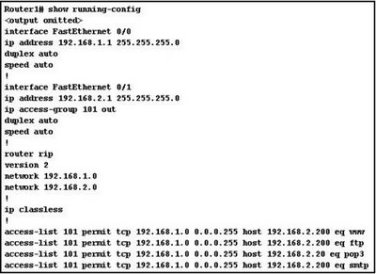 efer to the exhibit. Host 192.168.1.14 is unable to download email from 192.168.2.200. After reviewing the output of the show running-config command, what problem is discovered?
efer to the exhibit. Host 192.168.1.14 is unable to download email from 192.168.2.200. After reviewing the output of the show running-config command, what problem is discovered?
• Access to the SMTP server is denied.
• The destination host address in an ACL statement is incorrect.
• The ACL is applied to the interface in the wrong direction.
• The implicit deny any any is blocking all access to email.
11. An employee called the help desk to report a laptop that could not access a web-based application on the Internet. The help desk technician asked the employee to open a Windows command prompt and type the ipconfig /all command. Which problem-solving technique did the technician choose?
• top-down
• bottom-up
• substitution
• divide-and-conquer
12.

Refer to the exhibit. Based on the network diagram and the output shown, which statement is true?
• The command was entered on router R1.
• The command was entered on router R2.
• The command was entered on router R3.
• The command could have been entered on either R1 or R2.
13.

Refer to the exhibit. An ACL is configured to prevent access by network 192.168.1.0 to network 192.168.2.0, but it is not working properly. What problem is discovered after observing the output of the show running-config command?
• The protocol type specified in the ACL should be TCP, not IP.
• The source and destination addresses are reversed in the statement.
• The ACL is applied to the wrong interface, but the right direction.
• The ACL is applied to the wrong interface and the wrong direction.
• The permit ip any any statement allows network 192.168.1.0 access.
14.

Although all networks are reachable, the network administrator notices abnormal routing behavior after configuring OSPF on each router. According to the partial output from the debug ip ospf events command, which statement is true about the contents of the routing table in RA?
• It will show network 172.16.3.0 learned from RB.
• It will show network 172.16.3.0 learned from RC.
• It will show two equal routes to network 192.168.1.4/30.
• It will show two equal routes to network 192.168.1.8/30.
15. A network at a large building failed, causing a severe disruption in business activities. The problem was eventually detected and resolved by replacing a piece of failed network equipment. Investigation led to the conclusion that a network design problem was the main cause of the disruption. Loss of a single piece of equipment should not have been able to cause such a large problem. What two terms best describe this type of design weakness? (Choose two.)
• bottleneck
• limited availability
• limited scalability
• large failure domain
• single point of failure
• limited staff capabilities
16.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is troubleshooting the connectivity issue between RA and RB. According to the partial configuration, what is the cause of the problem?
• password mismatch for PPP authentication
• username mismatch for PPP authentication
• encapsulation method mismatch for PPP authentication
• authentication method mismatch for PPP authentication
17.

Refer to the exhibit. ABC Company is using the 172.16.0.0/18 network. It is standard company practice to use the first 50 addresses for switches and servers and assign the last usable address to the router. The remaining addresses are assigned to the hosts. After assigning the addresses, the network technician tests connectivity from the host above and is not able to ping the router. What could be the problem?
• The router was assigned the broadcast address.
• The host is not in the same subnet as the switch and router.
• The router interface is in the wrong subnet.
• The host was assigned a network address.
18.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a problem. No users are able to access the 10.10.2.0/24 network, but are able to access all other networks. Assuming R3 is configured correctly and based on the output shown, what is most likely the problem?
• There is congestion on the 10.10.2.0 network.
• The EIGRP process number on R2 is incorrect.
• The Fa0/0 interface on R2 is shut down.
• The Fa0/0 interface on R2 has an incorrect IP address or subnet mask.
19.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator correctly configures RTA to perform inter-VLAN routing. Using the show vlan command, the administrator verifies that port Fast Ethernet 0/4 is the first available port in the default VLAN on SW2. The administrator connects RTA to port 0/4 on SW2, but inter-VLAN routing does not work. What could be the possible cause of the problem with the SW2 configuration?
• Port 0/4 is not active.
• Port 0/4 must be a member of VLAN1.
• Port 0/4 is configured in access mode.
• Port 0/4 is configured as a trunk port.
20.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is unable to ping from the console of router R3 to host 10.10.4.63. What is the problem?
• RIPv1 does not support VLSM.
• Router R2 does not have RIP correctly configured.
• Router R3 is missing a network statement for network 10.0.0.0.
• There is an addressing problem on the link between routers R2 and R3.
21.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has implemented subnetting using the network 192.168.25.0 and a /28 mask. Workstation 1 is not able to ping with Workstation 2. What is a possible cause for this lack of communication?
• Workstation 1 and Workstation 2 are on the same subnet.
• The serial connections are using addresses from the LAN subnets.
• All hosts in the network must be in the same subnet to communicate.
• Workstation 1 is not on the same network that the RTA router LAN interface is on.
22. Which two statements describe when a network administrator should perform a network baseline? (Choose two.)
• It should be done monthly as a minimum standard.
• It should be performed when all switch Cisco IOS versions are upgraded.
• It should be done when all network printers are upgraded to a new model.
• It should be done when the network is performing at normal activity levels.
• It should be done whenever an SLA has been signed with a new service provider

Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output shown, to which IP network should the workstations in the Support department belong?
• 192.168.1.0
• 172.16.1.0
• 172.16.3.0
• 172.16.5.0
2.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is doing proactive network maintenance. The administrator pings 192.168.1.100 and compares the results to the baseline data. Based on the comparison of the two pings, what is one possibility?
• There is an ACL applied, making the destination host unreachable.
• There is a malfunctioning NIC on the destination host.
• The sending host is unable to access the network.
• There are congestion problems on the network.
3.

Refer to the exhibit. Given the output generated by the debug ppp negotiation command, which statement is true?
• The line protocol of the local router is now up.
• The username ’Goleta’ is configured locally.
• The command ppp authentication pap is configured on both routers.
• The local router requested to terminate the session.
4. What is important to consider while configuring the subinterfaces of a router when implementing inter-VLAN routing?
• The subinterface numbers must match the VLAN ID number.
• The physical interface must have an IP address configured.
• The IP address of each subinterface must be the default gateway address for each VLAN subnet.
• The no shutdown command must be given on each subinterface.
5.

Refer to the exhibit. A lab technician connects two routers together via a serial cable using the default interface configuration values. The interfaces are up; however, the technician is unable to ping between the two devices. What is the most likely problem?
• The lab technician used the wrong cable to connect the serial ports.
• There is an IP mismatch between the serial ports.
• There is an encapsulation mismatch between the serial ports.
• No clock rate has been set on the DCE interface.
6.

Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output shown, why is VTP information unable to propagate the network?
• One of the two client mode switches must be reconfigured to Transparent mode.
• Each switch must be synchronized to the network time server.
• The VTP domain names are different.
• VTP passwords must be set.
• The configuration revision numbers are all the same.
7. The enterprise mail server software recently went through a minor update. A network administrator notices an excessive amount of traffic between a database server and the newly updated mail server, compared to the baseline data. What is the first action the administrator should do to investigate the problem?
• Wait to see if the recent update will stabilize after a while.
• Redo the baseline data to include the minor upgrade.
• Check the log to see what software components are producing the excess traffic.
• Check for viruses and spyware on the database server.
8.

Refer to the exhibit. Users are reporting that they cannot access the Internet. Routers R1 and R2 are configured with RIP version 2 as shown. If R2 receives a packet with a destination address on the Internet, how is the packet routed?
• The packet is routed to the ISP router and then to network 10.1.1.0/24.
• The packet is routed to the ISP router and then to the Internet.
• The packet is routed to R1 and then forwarded out Fa0/0 on R1.
• The packet will not be routed because R2 does not have a valid default route.
9.

Refer to the exhibit. Both routers are configured using RIPv1. Both routers are sending updates about the directly connected routes. R1 can successfully ping the serial interface of R2. The routing table on R1 does not contain any dynamically learned routes from R2, and the routing table on R2 shows no dynamically learned routes from R1. What is the problem?
• Subnetting is not supported by RIPv1.
• One of the routers needs a clock rate on the serial interface.
• The serial link between the two routers is unstable.
• VLSM is not supported by RIPv1.
10.
R
 efer to the exhibit. Host 192.168.1.14 is unable to download email from 192.168.2.200. After reviewing the output of the show running-config command, what problem is discovered?
efer to the exhibit. Host 192.168.1.14 is unable to download email from 192.168.2.200. After reviewing the output of the show running-config command, what problem is discovered?• Access to the SMTP server is denied.
• The destination host address in an ACL statement is incorrect.
• The ACL is applied to the interface in the wrong direction.
• The implicit deny any any is blocking all access to email.
11. An employee called the help desk to report a laptop that could not access a web-based application on the Internet. The help desk technician asked the employee to open a Windows command prompt and type the ipconfig /all command. Which problem-solving technique did the technician choose?
• top-down
• bottom-up
• substitution
• divide-and-conquer
12.

Refer to the exhibit. Based on the network diagram and the output shown, which statement is true?
• The command was entered on router R1.
• The command was entered on router R2.
• The command was entered on router R3.
• The command could have been entered on either R1 or R2.
13.

Refer to the exhibit. An ACL is configured to prevent access by network 192.168.1.0 to network 192.168.2.0, but it is not working properly. What problem is discovered after observing the output of the show running-config command?
• The protocol type specified in the ACL should be TCP, not IP.
• The source and destination addresses are reversed in the statement.
• The ACL is applied to the wrong interface, but the right direction.
• The ACL is applied to the wrong interface and the wrong direction.
• The permit ip any any statement allows network 192.168.1.0 access.
14.

Although all networks are reachable, the network administrator notices abnormal routing behavior after configuring OSPF on each router. According to the partial output from the debug ip ospf events command, which statement is true about the contents of the routing table in RA?
• It will show network 172.16.3.0 learned from RB.
• It will show network 172.16.3.0 learned from RC.
• It will show two equal routes to network 192.168.1.4/30.
• It will show two equal routes to network 192.168.1.8/30.
15. A network at a large building failed, causing a severe disruption in business activities. The problem was eventually detected and resolved by replacing a piece of failed network equipment. Investigation led to the conclusion that a network design problem was the main cause of the disruption. Loss of a single piece of equipment should not have been able to cause such a large problem. What two terms best describe this type of design weakness? (Choose two.)
• bottleneck
• limited availability
• limited scalability
• large failure domain
• single point of failure
• limited staff capabilities
16.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is troubleshooting the connectivity issue between RA and RB. According to the partial configuration, what is the cause of the problem?
• password mismatch for PPP authentication
• username mismatch for PPP authentication
• encapsulation method mismatch for PPP authentication
• authentication method mismatch for PPP authentication
17.

Refer to the exhibit. ABC Company is using the 172.16.0.0/18 network. It is standard company practice to use the first 50 addresses for switches and servers and assign the last usable address to the router. The remaining addresses are assigned to the hosts. After assigning the addresses, the network technician tests connectivity from the host above and is not able to ping the router. What could be the problem?
• The router was assigned the broadcast address.
• The host is not in the same subnet as the switch and router.
• The router interface is in the wrong subnet.
• The host was assigned a network address.
18.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a problem. No users are able to access the 10.10.2.0/24 network, but are able to access all other networks. Assuming R3 is configured correctly and based on the output shown, what is most likely the problem?
• There is congestion on the 10.10.2.0 network.
• The EIGRP process number on R2 is incorrect.
• The Fa0/0 interface on R2 is shut down.
• The Fa0/0 interface on R2 has an incorrect IP address or subnet mask.
19.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator correctly configures RTA to perform inter-VLAN routing. Using the show vlan command, the administrator verifies that port Fast Ethernet 0/4 is the first available port in the default VLAN on SW2. The administrator connects RTA to port 0/4 on SW2, but inter-VLAN routing does not work. What could be the possible cause of the problem with the SW2 configuration?
• Port 0/4 is not active.
• Port 0/4 must be a member of VLAN1.
• Port 0/4 is configured in access mode.
• Port 0/4 is configured as a trunk port.
20.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is unable to ping from the console of router R3 to host 10.10.4.63. What is the problem?
• RIPv1 does not support VLSM.
• Router R2 does not have RIP correctly configured.
• Router R3 is missing a network statement for network 10.0.0.0.
• There is an addressing problem on the link between routers R2 and R3.
21.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has implemented subnetting using the network 192.168.25.0 and a /28 mask. Workstation 1 is not able to ping with Workstation 2. What is a possible cause for this lack of communication?
• Workstation 1 and Workstation 2 are on the same subnet.
• The serial connections are using addresses from the LAN subnets.
• All hosts in the network must be in the same subnet to communicate.
• Workstation 1 is not on the same network that the RTA router LAN interface is on.
22. Which two statements describe when a network administrator should perform a network baseline? (Choose two.)
• It should be done monthly as a minimum standard.
• It should be performed when all switch Cisco IOS versions are upgraded.
• It should be done when all network printers are upgraded to a new model.
• It should be done when the network is performing at normal activity levels.
• It should be done whenever an SLA has been signed with a new service provider
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 8 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to add the command deny ip 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 any log to R3. After adding the command, the administrator verifies the change using the show access-list command. What sequence number does the new entry have?
• 0
• 10, and all other items are shifted down to the next sequence number
• 50
• 60
2.
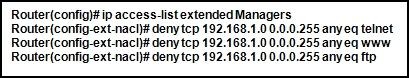
Refer to the exhibit. What happens if the network administrator issues the commands shown when an ACL called Managers already exists on the router?
• The new commands overwrite the current Managers ACL.
• The new commands are added to the end of the current Managers ACL.
• The new commands are added to the beginning of the current Managers ACL.
• An error appears stating that the ACL already exists.
3. Why are inbound ACLs more efficient for the router than outbound ACLs?
• Inbound ACLs deny packets before routing lookups are required.
• Inbound ACL operation requires less network bandwidth than outbound.
• Inbound ACLs permit or deny packets to LANs, which are typically more efficient than WANs.
• Inbound ACLs are applied to Ethernet interfaces, while outbound ACLs are applied to slower serial interfaces.
4.
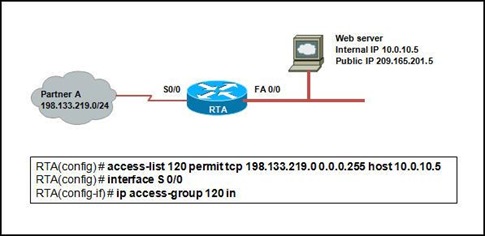
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator of a company needs to configure the router RTA to allow its business partner (Partner A) to access the web server located in the internal network. The web server is assigned a private IP address, and a static NAT is configured on the router for its public IP address. Finally, the administrator adds the ACL. However, Partner A is denied access to the web server. What is the cause of the problem?
• Port 80 should be specified in the ACL.
• The public IP address of the server, 209.165.201.5, should be specified as the destination.
• The ACL should be applied on the s0/0 outbound interface.
• The source address should be specified as 198.133.219.0 255.255.255.0 in the ACL.
5. ACL logging generates what type of syslog message?
• unstable network
• warning
• informational
• critical situation
6. Which two host addresses are included in the range specified by 172.16.31.64 0.0.0.31? (Choose two.)
• 172.16.31.64
• 172.16.31.77
• 172.16.31.78
• 172.16.31.95
• 172.16.31.96
7. Traffic from the 64.104.48.0 to 64.104.63.255 range must be denied access to the network. What wildcard mask would the network administrator configure in the access list to cover this range?
• 0.0.15.255
• 0.0.47.255
• 0.0.63.255
• 255.255.240.0
8. ACLs are used primarily to filter traffic. What are two additional uses of ACLs? (Choose two.)
• specifying source addresses for authentication
• specifying internal hosts for NAT
• identifying traffic for QoS
• reorganizing traffic into VLANs
• filtering VTP packets
9. What can an administrator do to ensure that ICMP DoS attacks from the outside are mitigated as much as possible, without hampering connectivity tests initiated from the inside out?
• Create an access list permitting only echo reply and destination unreachable packets from the outside.
• Create an access list denying all ICMP traffic coming from the outside.
• Permit ICMP traffic from only known external sources.
• Create an access list with the established keyword at the end of the line.
10. What effect does the command reload in 30 have when entered into a router?
• If a router process freezes, the router reloads automatically.
• If a packet from a denied source attempts to enter an interface where an ACL is applied, the router reloads in 30 minutes.
• If a remote connection lasts for longer than 30 minutes, the router forces the remote user off.
• A router automatically reloads in 30 minutes.
11.

Refer to the exhibit. The following commands were entered on RTB.
RTB(config)# access-list 4 deny 192.168.20.16 0.0.0.15
RTB(config)# access-list 4 permit any
RTB(config)# interface serial 0/0/0
RTB(config-if)# ip access-group 4 in
Which addresses do these commands block access to RTB?
• 192.168.20.17 to 192.168.20.31
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.31*
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.32
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.33
12.
Refer to the exhibit. The new security policy for the company allows all IP traffic from the Engineering LAN to the Internet while only web traffic from the Marketing LAN is allowed to the Internet. Which ACL can be applied in the outbound direction of Serial 0/1 on the Marketing router to implement the new security policy?
• access-list 197 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 197 permit ip 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
• access-list 165 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 165 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
access-list 165 permit ip any any
• access-list 137 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 137 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
• access-list 89 permit 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 89 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
13. Which three statements are true concerning standard and extended ACLs? (Choose three.)
• Extended ACLs are usually placed so that all packets go through the network and are filtered at the destination.
• Standard ACLs are usually placed so that all packets go through the network and are filtered at the destination.
• Extended ACLs filter based on source address only, and must be placed near the destination if other traffic is to flow.
• Standard ACLs filter based on source address only, and must be placed near the destination if other traffic is to flow.
• Extended ACLs filter with many possible factors, and they allow only desired packets to pass through the network if placed near the source.
• Standard ACLs filter with many possible factors, and they allow only desired packets to pass through the network if placed near the source.
14.

Refer to the exhibit. Company policy for the network that is shown indicates the following guidelines:
1) All hosts on the 192.168.3.0/24 network, except host 192.168.3.77, should be able to reach the 192.168.2.0/24 network.
2) All hosts on the 192.168.3.0/24 network should be able to reach the 192.168.1.0/24 network.
3) All other traffic originating from the 192.168.3.0 network should be denied.
Which set of ACL statements meets the stated requirements when they are applied to the Fa0/0 interface of router R2 in the inbound direction?
• access-list 101 deny ip any any
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip any any
• access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
15.
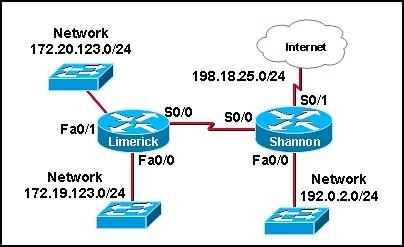
Hosts from the Limerick LAN are not allowed access to the Shannon LAN but should be able to access the Internet. Which set of commands will create a standard ACL that will apply to traffic on the Shannon router interface Fa0/0 implementing this security?
• access-list 42 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.255 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 42 permit any
• access-list 56 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 56 permit any
• access-list 61 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.0
access-list 61 permit any
• access-list 87 deny ip any 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 87 permit ip any
16.
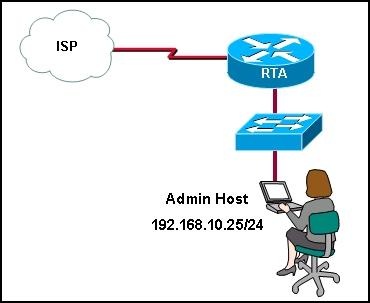
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure an access list that will allow the management host with an IP address of 192.168.10.25/24 to be the only host to remotely access and configure router RTA. All vty and enable passwords are configured on the router. Which group of commands will accomplish this task?
• Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any 192.168.10.25 0.0.0.0 eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip any any
Router(config)# int s0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
Router(config-if)# int fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ip access-group 101 in
• Router(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.10.25 eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 10 deny any
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)#access-group 10 in
• Router(config)# access-list 86 permit host 192.168.10.25
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)# access-class 86 in
• Router(config)# access-list 125 permit tcp 192.168.10.25 any eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 125 deny ip any any
Router(config)# int s0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 125 in
17. Which ACL permits host 10.220.158.10 access to the web server 192.168.3.244?
• access-list 101 permit tcp host 10.220.158.10 eq 80 host 192.168.3.224
• access-list 101 permit tcp 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 0.0.0.0 eq 80
• access-list 101 permit host 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 0.0.0.0 eq 80
• access-list 101 permit tcp 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 eq 80
18. Which wildcard mask would match the host range for the subnet 192.16.5.32 /27?
• 0.0.0.32
• 0.0.0.63
• 0.0.63.255
• 0.0.0.31
19. A security administrator wants to secure password exchanges on the vty lines on all routers in the enterprise. What option should be implemented to ensure that passwords are not sent in clear text across the public network?
• Use Telnet with an authentication server to ensure effective authentication.
• Apply an access list on the router interfaces to allow only authorized computers.
• Apply an access list on the vty line to allow only authorized computers.
• Use only Secure Shell (SSH) on the vty lines.
20.

Refer to the exhibit. An administrator notes a significant increase in the amount of traffic entering the network from the ISP. The administrator clears the access-list counters. After a few minutes, the administrator again checks the access-list table. What can be concluded from the most recent output shown?
• A small amount of HTTP trafic is an indication that the web server was not configured correctly.
• A larger amount of POP3 traffic (compared with SMTP traffic) indicates that there are more POP3 email clients than SMTP clients in the enterprise.
• A large amount of ICMP traffic is being denied at the interface, which can be an indication of a DoS attack.
• A larger amount of email traffic (compared with web traffic) is an indication that attackers mainly targeted the email server.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to add the command deny ip 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 any log to R3. After adding the command, the administrator verifies the change using the show access-list command. What sequence number does the new entry have?
• 0
• 10, and all other items are shifted down to the next sequence number
• 50
• 60
2.

Refer to the exhibit. What happens if the network administrator issues the commands shown when an ACL called Managers already exists on the router?
• The new commands overwrite the current Managers ACL.
• The new commands are added to the end of the current Managers ACL.
• The new commands are added to the beginning of the current Managers ACL.
• An error appears stating that the ACL already exists.
3. Why are inbound ACLs more efficient for the router than outbound ACLs?
• Inbound ACLs deny packets before routing lookups are required.
• Inbound ACL operation requires less network bandwidth than outbound.
• Inbound ACLs permit or deny packets to LANs, which are typically more efficient than WANs.
• Inbound ACLs are applied to Ethernet interfaces, while outbound ACLs are applied to slower serial interfaces.
4.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator of a company needs to configure the router RTA to allow its business partner (Partner A) to access the web server located in the internal network. The web server is assigned a private IP address, and a static NAT is configured on the router for its public IP address. Finally, the administrator adds the ACL. However, Partner A is denied access to the web server. What is the cause of the problem?
• Port 80 should be specified in the ACL.
• The public IP address of the server, 209.165.201.5, should be specified as the destination.
• The ACL should be applied on the s0/0 outbound interface.
• The source address should be specified as 198.133.219.0 255.255.255.0 in the ACL.
5. ACL logging generates what type of syslog message?
• unstable network
• warning
• informational
• critical situation
6. Which two host addresses are included in the range specified by 172.16.31.64 0.0.0.31? (Choose two.)
• 172.16.31.64
• 172.16.31.77
• 172.16.31.78
• 172.16.31.95
• 172.16.31.96
7. Traffic from the 64.104.48.0 to 64.104.63.255 range must be denied access to the network. What wildcard mask would the network administrator configure in the access list to cover this range?
• 0.0.15.255
• 0.0.47.255
• 0.0.63.255
• 255.255.240.0
8. ACLs are used primarily to filter traffic. What are two additional uses of ACLs? (Choose two.)
• specifying source addresses for authentication
• specifying internal hosts for NAT
• identifying traffic for QoS
• reorganizing traffic into VLANs
• filtering VTP packets
9. What can an administrator do to ensure that ICMP DoS attacks from the outside are mitigated as much as possible, without hampering connectivity tests initiated from the inside out?
• Create an access list permitting only echo reply and destination unreachable packets from the outside.
• Create an access list denying all ICMP traffic coming from the outside.
• Permit ICMP traffic from only known external sources.
• Create an access list with the established keyword at the end of the line.
10. What effect does the command reload in 30 have when entered into a router?
• If a router process freezes, the router reloads automatically.
• If a packet from a denied source attempts to enter an interface where an ACL is applied, the router reloads in 30 minutes.
• If a remote connection lasts for longer than 30 minutes, the router forces the remote user off.
• A router automatically reloads in 30 minutes.
11.

Refer to the exhibit. The following commands were entered on RTB.
RTB(config)# access-list 4 deny 192.168.20.16 0.0.0.15
RTB(config)# access-list 4 permit any
RTB(config)# interface serial 0/0/0
RTB(config-if)# ip access-group 4 in
Which addresses do these commands block access to RTB?
• 192.168.20.17 to 192.168.20.31
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.31*
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.32
• 192.168.20.16 to 192.168.20.33
12.
Refer to the exhibit. The new security policy for the company allows all IP traffic from the Engineering LAN to the Internet while only web traffic from the Marketing LAN is allowed to the Internet. Which ACL can be applied in the outbound direction of Serial 0/1 on the Marketing router to implement the new security policy?
• access-list 197 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 197 permit ip 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
• access-list 165 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 165 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
access-list 165 permit ip any any
• access-list 137 permit ip 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 137 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
• access-list 89 permit 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 any
access-list 89 permit tcp 198.18.112.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
13. Which three statements are true concerning standard and extended ACLs? (Choose three.)
• Extended ACLs are usually placed so that all packets go through the network and are filtered at the destination.
• Standard ACLs are usually placed so that all packets go through the network and are filtered at the destination.
• Extended ACLs filter based on source address only, and must be placed near the destination if other traffic is to flow.
• Standard ACLs filter based on source address only, and must be placed near the destination if other traffic is to flow.
• Extended ACLs filter with many possible factors, and they allow only desired packets to pass through the network if placed near the source.
• Standard ACLs filter with many possible factors, and they allow only desired packets to pass through the network if placed near the source.
14.

Refer to the exhibit. Company policy for the network that is shown indicates the following guidelines:
1) All hosts on the 192.168.3.0/24 network, except host 192.168.3.77, should be able to reach the 192.168.2.0/24 network.
2) All hosts on the 192.168.3.0/24 network should be able to reach the 192.168.1.0/24 network.
3) All other traffic originating from the 192.168.3.0 network should be denied.
Which set of ACL statements meets the stated requirements when they are applied to the Fa0/0 interface of router R2 in the inbound direction?
• access-list 101 deny ip any any
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
• access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip any any
• access-list 101 deny ip 192.168.3.77 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
15.

Hosts from the Limerick LAN are not allowed access to the Shannon LAN but should be able to access the Internet. Which set of commands will create a standard ACL that will apply to traffic on the Shannon router interface Fa0/0 implementing this security?
• access-list 42 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.255 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 42 permit any
• access-list 56 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 56 permit any
• access-list 61 deny 172.19.123.0 0.0.0.0
access-list 61 permit any
• access-list 87 deny ip any 192.0.2.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 87 permit ip any
16.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator needs to configure an access list that will allow the management host with an IP address of 192.168.10.25/24 to be the only host to remotely access and configure router RTA. All vty and enable passwords are configured on the router. Which group of commands will accomplish this task?
• Router(config)# access-list 101 permit tcp any 192.168.10.25 0.0.0.0 eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip any any
Router(config)# int s0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
Router(config-if)# int fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ip access-group 101 in
• Router(config)# access-list 10 permit 192.168.10.25 eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 10 deny any
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)#access-group 10 in
• Router(config)# access-list 86 permit host 192.168.10.25
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)# access-class 86 in
• Router(config)# access-list 125 permit tcp 192.168.10.25 any eq telnet
Router(config)# access-list 125 deny ip any any
Router(config)# int s0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 125 in
17. Which ACL permits host 10.220.158.10 access to the web server 192.168.3.244?
• access-list 101 permit tcp host 10.220.158.10 eq 80 host 192.168.3.224
• access-list 101 permit tcp 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 0.0.0.0 eq 80
• access-list 101 permit host 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 0.0.0.0 eq 80
• access-list 101 permit tcp 10.220.158.10 0.0.0.0 host 192.168.3.224 eq 80
18. Which wildcard mask would match the host range for the subnet 192.16.5.32 /27?
• 0.0.0.32
• 0.0.0.63
• 0.0.63.255
• 0.0.0.31
19. A security administrator wants to secure password exchanges on the vty lines on all routers in the enterprise. What option should be implemented to ensure that passwords are not sent in clear text across the public network?
• Use Telnet with an authentication server to ensure effective authentication.
• Apply an access list on the router interfaces to allow only authorized computers.
• Apply an access list on the vty line to allow only authorized computers.
• Use only Secure Shell (SSH) on the vty lines.
20.

Refer to the exhibit. An administrator notes a significant increase in the amount of traffic entering the network from the ISP. The administrator clears the access-list counters. After a few minutes, the administrator again checks the access-list table. What can be concluded from the most recent output shown?
• A small amount of HTTP trafic is an indication that the web server was not configured correctly.
• A larger amount of POP3 traffic (compared with SMTP traffic) indicates that there are more POP3 email clients than SMTP clients in the enterprise.
• A large amount of ICMP traffic is being denied at the interface, which can be an indication of a DoS attack.
• A larger amount of email traffic (compared with web traffic) is an indication that attackers mainly targeted the email server.
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 7 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1. Why are Network Control Protocols used in PPP?
• to establish and terminate data links
• to provide authentication capabilities to PPP
• to manage network congestion and to allow quality testing of the link
• to allow multiple Layer 3 protocols to operate over the same physical link
2. What is the data transmission rate for the DS0 standard?
• 44 kb/s
• 64 kb/s
• 1.544 Mb/s
• 44.736 Mb/s
3. In which two layers of the OSI model are key differences found between a LAN and a WAN. (Choose two.)
• Layer 1
• Layer 2
• Layer 3
• Layer 4
• Layer 6
• Layer 7
4. Which statement is true about the Cisco implementation of the HDLC protocol?
• It supports authentication.
• It has a universally compatible frame format.
• It is the default encapsulation for serial interfaces on Cisco routers.
• It does not support multiple protocols across a single link.
5.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has a connectivity problem between the serial interfaces of Merida and Vargas. What is the cause of the problem?
• Authentication is required on the serial link.
• The encapsulation is misconfigured.
• The IP addresses are on different subnets.
• The serial interface on Vargas is shutdown.
• The loopback interfaces on both routers are not configured.
6.

Refer to the exhibit. What statement is true about the exhibited output?
• LCP is in the process of negotiating a link.
• LCP and NCP are waiting for CHAP authentication to complete.
• LCP negotiation has completed successfully, but NCP negotiation is in progress.
• LCP and NCP negotiation is complete, and the data link service is available to carry packets.
7. Which three statements are true regarding LCP? (Choose three.)
• It is responsible for negotiating link establishment.
• It negotiates options for Layer 3 protocols running over PPP.
• It uses MD5 encryption while negotiating link-establishment parameters.
• It terminates the link upon user request or the expiration of an inactivity timer.
• It can test the link to determine if link quality is sufficient to bring up the link.
• It monitors the link for congestion and dynamically adjusts the acceptable window size.
8. Why are Frame Relay paths referred to as virtual?
• Frame Relay PVCs are created and discarded on demand.
• The connections between PVC endpoints act like dialup circuits.
• There are no dedicated circuits to and from the Frame Relay carrier.
• The physical circuits inside the Frame Relay cloud do not contain exclusive links for a specific Frame Relay connection.
9. What best describes the use of a data-link connection identifier (DLCI)?
• an address identifying a virtual circuit
• a logical address identifying the DCE device
• an address identifying a Layer 3 service across a Frame Relay network
• a logical address identifying the physical interface between a router and a Frame Relay switch
10. What two services allow the router to dynamically map data link layer addresses to network layer addresses Frame Relay network? (Choose two.)
• ARP
• ICMP
• Proxy ARP
• Inverse ARP
• LMI status messages
11. Which three statements describe functions of the Point-to-Point Protocol with regards to the OSI model?(Choose three.)
• operates at all layers of the OSI model
• provides a mechanism to multiplex several network layer protocols
• can be configured on both synchronous and asynchronous serial interfaces
• uses Layer 3 of the OSI model to establish and maintain a session between devices
• uses the data link layer to configure such options as error detection and compression
• uses network control protocols to test and maintain connectivity between devices
12. At what physical location does the responsibility for a WAN connection change from the user to the service provider?
• demilitarized zone (DMZ)
• demarcation point
• local loop
• cloud
13. What does a Frame Relay switch use to inform the sender that there is congestion?
• FECN
• BECN
• DE
• FCS
14.

Refer to the exhibit. What statement is true about the debug output?
• R2 is using PAP instead of CHAP.
• The routers have different CHAP passwords configured.
• The administrator performed a shutdown on the R2 PPP interface during negotiation.
• The Layer 3 protocol negotiation caused the connection failure.
15. Which two statements describe the function of time-division multiplexing? (Choose two.)
• Multiple data streams share one common channel.
• Conversations that require extra bandwidth receive any unused time slices.
• Time slots are utilized on a first-come, first-served basis.
• Time slots go unused if a sender has nothing to transmit.
• Priority can be dedicated to one data source.
16. When customers use credit cards to make purchases at a small business, a modem is heard dialing a telephone number to transfer the transaction data to the central office. What type of WAN serial connection is in use?
• leased line
• point-to-point
• circuit switched
• packet switched
17. Which best describes data communications equipment (DCE)?
• serves as data source and/or destination
• responsible for negotiating windowing and acknowledgements
• physical devices such as protocol translators and multiplexers
• equipment that forwards data and is responsible for the clocking signal
18. Permanent virtual circuits and switched virtual circuits are both part of which option for WAN connectivity?
• leased line
• cell switching
• packet switching
• circuit switching
19. Which field of a frame uses error detection mechanisms to verify that the frame is not damaged intransit?
• FCS
• MTU
• flag
• control
• protocol
20. What occurs in the encapsulation process as a data packet moves from a LAN across a WAN?
• The Layer 2 encapsulation changes to a format that is appropriate for the WAN technology.
• The Layer 3 encapsulation changes to a format that is appropriate for the WAN technology.
• Both Layer 2 and Layer 3 encapsulation change to a technology that is appropriate for the WAN.
• Both Layer 2 and Layer 3 encapsulation remain constant as the data packet travels throughout the network.
21.
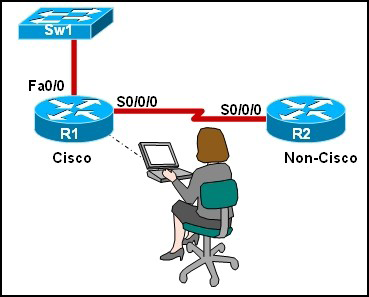
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is configuring R1 to connect to R2, which is a non-Cisco router. Which encapsulation method will need to be configured for communication to occur?
• HDLC
• HSSI
• ISDN
• IPCP
• PPP
22. A company is implementing dialup services for remote workers to connect to the local network. The company uses multiple Layer 3 protocols and requires authentication for security. Which protocol should be used for this remote access?
• LMI
• PPP
• HDLC
• Frame Relay
23. Which two options can LCP negotiate? (Choose two.)
• compression
• authentication
• dynamic flow control
• network layer address for IP
• connection-oriented or connectionless communication methods
24. What statement best describes cell switching?
• It uses a dedicated path between endpoints.
• It creates a permanent physical link between two points.
• It uses DLCIs to identify virtual circuits.
• It creates fixed-length packets that traverse virtual circuits
• to establish and terminate data links
• to provide authentication capabilities to PPP
• to manage network congestion and to allow quality testing of the link
• to allow multiple Layer 3 protocols to operate over the same physical link
2. What is the data transmission rate for the DS0 standard?
• 44 kb/s
• 64 kb/s
• 1.544 Mb/s
• 44.736 Mb/s
3. In which two layers of the OSI model are key differences found between a LAN and a WAN. (Choose two.)
• Layer 1
• Layer 2
• Layer 3
• Layer 4
• Layer 6
• Layer 7
4. Which statement is true about the Cisco implementation of the HDLC protocol?
• It supports authentication.
• It has a universally compatible frame format.
• It is the default encapsulation for serial interfaces on Cisco routers.
• It does not support multiple protocols across a single link.
5.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has a connectivity problem between the serial interfaces of Merida and Vargas. What is the cause of the problem?
• Authentication is required on the serial link.
• The encapsulation is misconfigured.
• The IP addresses are on different subnets.
• The serial interface on Vargas is shutdown.
• The loopback interfaces on both routers are not configured.
6.

Refer to the exhibit. What statement is true about the exhibited output?
• LCP is in the process of negotiating a link.
• LCP and NCP are waiting for CHAP authentication to complete.
• LCP negotiation has completed successfully, but NCP negotiation is in progress.
• LCP and NCP negotiation is complete, and the data link service is available to carry packets.
7. Which three statements are true regarding LCP? (Choose three.)
• It is responsible for negotiating link establishment.
• It negotiates options for Layer 3 protocols running over PPP.
• It uses MD5 encryption while negotiating link-establishment parameters.
• It terminates the link upon user request or the expiration of an inactivity timer.
• It can test the link to determine if link quality is sufficient to bring up the link.
• It monitors the link for congestion and dynamically adjusts the acceptable window size.
8. Why are Frame Relay paths referred to as virtual?
• Frame Relay PVCs are created and discarded on demand.
• The connections between PVC endpoints act like dialup circuits.
• There are no dedicated circuits to and from the Frame Relay carrier.
• The physical circuits inside the Frame Relay cloud do not contain exclusive links for a specific Frame Relay connection.
9. What best describes the use of a data-link connection identifier (DLCI)?
• an address identifying a virtual circuit
• a logical address identifying the DCE device
• an address identifying a Layer 3 service across a Frame Relay network
• a logical address identifying the physical interface between a router and a Frame Relay switch
10. What two services allow the router to dynamically map data link layer addresses to network layer addresses Frame Relay network? (Choose two.)
• ARP
• ICMP
• Proxy ARP
• Inverse ARP
• LMI status messages
11. Which three statements describe functions of the Point-to-Point Protocol with regards to the OSI model?(Choose three.)
• operates at all layers of the OSI model
• provides a mechanism to multiplex several network layer protocols
• can be configured on both synchronous and asynchronous serial interfaces
• uses Layer 3 of the OSI model to establish and maintain a session between devices
• uses the data link layer to configure such options as error detection and compression
• uses network control protocols to test and maintain connectivity between devices
12. At what physical location does the responsibility for a WAN connection change from the user to the service provider?
• demilitarized zone (DMZ)
• demarcation point
• local loop
• cloud
13. What does a Frame Relay switch use to inform the sender that there is congestion?
• FECN
• BECN
• DE
• FCS
14.

Refer to the exhibit. What statement is true about the debug output?
• R2 is using PAP instead of CHAP.
• The routers have different CHAP passwords configured.
• The administrator performed a shutdown on the R2 PPP interface during negotiation.
• The Layer 3 protocol negotiation caused the connection failure.
15. Which two statements describe the function of time-division multiplexing? (Choose two.)
• Multiple data streams share one common channel.
• Conversations that require extra bandwidth receive any unused time slices.
• Time slots are utilized on a first-come, first-served basis.
• Time slots go unused if a sender has nothing to transmit.
• Priority can be dedicated to one data source.
16. When customers use credit cards to make purchases at a small business, a modem is heard dialing a telephone number to transfer the transaction data to the central office. What type of WAN serial connection is in use?
• leased line
• point-to-point
• circuit switched
• packet switched
17. Which best describes data communications equipment (DCE)?
• serves as data source and/or destination
• responsible for negotiating windowing and acknowledgements
• physical devices such as protocol translators and multiplexers
• equipment that forwards data and is responsible for the clocking signal
18. Permanent virtual circuits and switched virtual circuits are both part of which option for WAN connectivity?
• leased line
• cell switching
• packet switching
• circuit switching
19. Which field of a frame uses error detection mechanisms to verify that the frame is not damaged intransit?
• FCS
• MTU
• flag
• control
• protocol
20. What occurs in the encapsulation process as a data packet moves from a LAN across a WAN?
• The Layer 2 encapsulation changes to a format that is appropriate for the WAN technology.
• The Layer 3 encapsulation changes to a format that is appropriate for the WAN technology.
• Both Layer 2 and Layer 3 encapsulation change to a technology that is appropriate for the WAN.
• Both Layer 2 and Layer 3 encapsulation remain constant as the data packet travels throughout the network.
21.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is configuring R1 to connect to R2, which is a non-Cisco router. Which encapsulation method will need to be configured for communication to occur?
• HDLC
• HSSI
• ISDN
• IPCP
• PPP
22. A company is implementing dialup services for remote workers to connect to the local network. The company uses multiple Layer 3 protocols and requires authentication for security. Which protocol should be used for this remote access?
• LMI
• PPP
• HDLC
• Frame Relay
23. Which two options can LCP negotiate? (Choose two.)
• compression
• authentication
• dynamic flow control
• network layer address for IP
• connection-oriented or connectionless communication methods
24. What statement best describes cell switching?
• It uses a dedicated path between endpoints.
• It creates a permanent physical link between two points.
• It uses DLCIs to identify virtual circuits.
• It creates fixed-length packets that traverse virtual circuits
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 6 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1.

Refer to the exhibit. What statement describes the DR/BDR relationship of the HQ router?
• HQ is the DR.
• HQ is the BDR.
• HQ is a DROTHER.
• HQ is a member of an NBMA network.
2. Which two features are associated with Frame Relay OSPF point-to-multipoint environments? (Choose two.)
• A DR is not elected.
• The OSPF priority value determines the active DR on the Frame Relay link.
• OSPF neighbor routers are statically defined.
• The link types are identified as broadcast multiaccess.
• The BDR will have a router ID whose value is greater than the DR router ID.
3.

Refer to the exhibit. How was the OSPF default gateway entry for R2 determined?
• Default routes are automatically injected by OSPF into all advertisements.
• A static default gateway route is defined in the configuration of R2.
• The default-information originate command is applied on R1.
• The ISP defines the gateway of last resort and automatically passes it to R1 and R2.
• The ip default-gateway command is applied on R2.
4. What is always required for OSPF routers to share routing information?
• designated routers
• a backup designated router
• neighbor adjacencies
• an NBMA network topology
• links that are configured on the 224.0.0.0 network
5.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has implemented OSPF and the network has converged. If all router interfaces are enabled and functional, what route will OSPF view as lowest cost when moving frames from Host3 to Host1?
• R3 to R4 to R1
• R3 to R1
• R3 to R2 to R1
• R3 to R5 to R2 to R1
6.

Refer to the exhibit. Which commands configure router A for OSPF?
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.0
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
network 192.168.10.192 0.0.0.3 area 0
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192
network 192.168.10.192 255.255.255.252
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.0 area 0
7.

Refer to the exhibit. Which network statement configures the home router to allow all the interfaces to participate in OSPF?
• network 10.0.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0
• network 10.8.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
• network 10.8.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0
• network 10.10.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
• network 10.12.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0
8. Which statement is true regarding OSPF DR and BDR elections?
• A new DR/BDR election occurs each time a new OSPF neighbor is added.
• The router with the highest OSPF priority setting wins the election for DR.
• The default priority value for a router connected to a multi-access network is 0.
• The router with the highest MAC address is elected as the DR when the default priority values are used.
9.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator would like only the 172.16.32.0 network advertised to Router1. Which OSPF network command accomplishes this?
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.15 area 0
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.32.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.32.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
10. Which two statements describe the operation of link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
• All routers in the same area have identical link-state databases when converged.
• Routing loops are prevented by running the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL).
• Link-state routers send frequent periodic updates of the entire routing table.
• Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) is used to deliver and receive LSAs.
• Calculating the shortest path for each destination is accomplished with the SPF algorithm.
11.

Refer to the exhibit. Routers A, B, and C are part of the existing OSPF network. Router D has been added to the network. All routers are running OSPF and have the indicated priorities applied to the interface. What is the DR/BDR status immediately after router D is added to the existing network?
• An election is forced and router D wins the DR election.
• The DR and BDR do not change until the next election.
• An election is forced and the existing BDR becomes the DR.
• The router with the highest router ID becomes the new BDR.
12. Which two statements describe the use of OSPF DR/BDR elections? (Choose two.)
• Elections are always optional.
• Elections are required in all WAN networks.
• Elections are required in point-to-point networks.
• Elections are required in broadcast multiaccess networks.
• Elections are sometimes required in NBMA networks.
13.

Refer to the exhibit. As part of an OSPF network, R1 and R2 are trying to become adjacent neighbors. Although it appears that the two systems are communicating, neither of the routing tables include OSPF routes received from its neighbor. What could be responsible for this situation?
• R1 and R2 are not on the same subnet.
• The Process IDs on each router do not match.
• The timer intervals on the routers do not match.
• The value set for the Transmit Delay time on both routers is too low.
14.

Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the value 128 shown in bold?
• It is the OSPF cost metric.
• It is the OSPF administrative distance.
• It is the value assigned by the Dijkstra algorithm that designates the distance in hops to the network.
• It is the value assigned to an interface that is used by the DUAL algorithm to determine the metric.
15.

Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the configuration commands added on router B?
• allows router A to form an adjacency with router B
• provides a stable OSPF router ID on router B
• provides a method of testing router traffic
• creates the OSPF adjacency table on router B
16.

Refer to the exhibit. The command ip route 10.16.1.64 255.255.255.252 s0/0/0 is entered into the router. Why does network 10.16.1.64/30 appear in the routing table in addition to network 10.16.1.64/27?
• The router views 10.16.1.64/30 and 10.16.1.64/27 as two different networks.
• The static route is used as a backup route for packets destined for 10.16.1.64/27.
• The AD for static routes is lower than the AD for OSPF routes.
• The static route metric is lower than the OSPF metric for the 10.16.1.64/27 network.
17. What is the primary difference between link-state protocols and distance vector protocols with regard to route calculation?
• Distance vector protocols take existing routes from their neighbors and add to them. Link-state protocols independently calculate full routes.
• Link-state protocols calculate and pass full routing tables to all routers in their associated areas, and distance vector protocols do not.
• When determining invalid routes, link-state protocols use split horizon for all route computations. Distance vector protocols use reverse poisoning.
• Distance vector protocols require more CPU and RAM for route calculations than link-state protocols require.
18. What range of networks are advertised in the OSPF updates by the command Router1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0?
• 192.168.0.0/24 through 192.168.0.15/24
• 192.168.0.0/24 through 192.168.15.0/24
• 192.168.15.0/24 through 192.168.31.0/24
• 192.168.15.0/24 through 192.168.255.0/24
• 192.168.16.0/24 through 192.168.255.0/24
19.

Refer to the exhibit. When establishing adjacency relationships, which IP address would router A use to send hello packets to router B?
• 10.11.0.1
• 10.11.0.2
• 10.11.0.255
• 224.0.0.5
• 255.255.255.255
20.

Refer to the exhibit. Which router will be elected the DR and which will become the BDR?
• R1 will be DR and R2 will be BDR.
• R1 will be DR and R3 will be BDR.
• R2 will be DR and R1 will be BDR.
• R2 will be DR and R3 will be BDR.
• R3 will be DR and R2 will be BDR.
• R3 will be DR and R1 will be BDR.
21. When compared to a distance vector routing protocol, what is a benefit of the hierarchical design approach that is used in large OSPF networks?
• simpler configuration
• reduction of router processing requirements
• isolation of network instability
• less complex network planning
22. What are two advantages of using a link-state routing protocol instead of a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two.)
• The topology database eliminates the need for a routing table.
• Frequent periodic updates are sent to minimize the number of incorrect routes in the topological database.
• Routers have direct knowledge of all links in the network and how they are connected.
• After the initial LSA flooding, routers generally require less bandwidth to communicate changes in a topology.
• A link-state routing protocol requires less router processor power.
23. If a network has converged, what is true about the link-state database held by each router in the same OSPF area?
• Each router has a link-state database containing the same status information.
• Each router has a different link-state database depending on its position within the network.
• The link-state database is stored in a designated router and is accessed by each router in the area as needed.
• The link-state database in each router only contains information about adjacent routers and the status of their links.
24.

Refer to the exhibit. RTRC was recently configured and is not sending the proper OSPF routes to RTRB, as shown in the RTRB routing table. Based on the RTRC configuration, what is most likely the problem?
• RTRC interfaces are administratively shut down.
• The OSPF process ID for RTRC does not match the process ID used on RTRB.
• The interface addresses on RTRC overlap with other addresses in the network.
• The OSPF routing configuration on RTRC has a missing or incorrect network statement.

Refer to the exhibit. What statement describes the DR/BDR relationship of the HQ router?
• HQ is the DR.
• HQ is the BDR.
• HQ is a DROTHER.
• HQ is a member of an NBMA network.
2. Which two features are associated with Frame Relay OSPF point-to-multipoint environments? (Choose two.)
• A DR is not elected.
• The OSPF priority value determines the active DR on the Frame Relay link.
• OSPF neighbor routers are statically defined.
• The link types are identified as broadcast multiaccess.
• The BDR will have a router ID whose value is greater than the DR router ID.
3.

Refer to the exhibit. How was the OSPF default gateway entry for R2 determined?
• Default routes are automatically injected by OSPF into all advertisements.
• A static default gateway route is defined in the configuration of R2.
• The default-information originate command is applied on R1.
• The ISP defines the gateway of last resort and automatically passes it to R1 and R2.
• The ip default-gateway command is applied on R2.
4. What is always required for OSPF routers to share routing information?
• designated routers
• a backup designated router
• neighbor adjacencies
• an NBMA network topology
• links that are configured on the 224.0.0.0 network
5.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has implemented OSPF and the network has converged. If all router interfaces are enabled and functional, what route will OSPF view as lowest cost when moving frames from Host3 to Host1?
• R3 to R4 to R1
• R3 to R1
• R3 to R2 to R1
• R3 to R5 to R2 to R1
6.

Refer to the exhibit. Which commands configure router A for OSPF?
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.0
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
network 192.168.10.192 0.0.0.3 area 0
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192
network 192.168.10.192 255.255.255.252
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.0 area 0
7.

Refer to the exhibit. Which network statement configures the home router to allow all the interfaces to participate in OSPF?
• network 10.0.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0
• network 10.8.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
• network 10.8.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0
• network 10.10.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
• network 10.12.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0
8. Which statement is true regarding OSPF DR and BDR elections?
• A new DR/BDR election occurs each time a new OSPF neighbor is added.
• The router with the highest OSPF priority setting wins the election for DR.
• The default priority value for a router connected to a multi-access network is 0.
• The router with the highest MAC address is elected as the DR when the default priority values are used.
9.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator would like only the 172.16.32.0 network advertised to Router1. Which OSPF network command accomplishes this?
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.15 area 0
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.32.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.32.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
10. Which two statements describe the operation of link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
• All routers in the same area have identical link-state databases when converged.
• Routing loops are prevented by running the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL).
• Link-state routers send frequent periodic updates of the entire routing table.
• Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) is used to deliver and receive LSAs.
• Calculating the shortest path for each destination is accomplished with the SPF algorithm.
11.

Refer to the exhibit. Routers A, B, and C are part of the existing OSPF network. Router D has been added to the network. All routers are running OSPF and have the indicated priorities applied to the interface. What is the DR/BDR status immediately after router D is added to the existing network?
• An election is forced and router D wins the DR election.
• The DR and BDR do not change until the next election.
• An election is forced and the existing BDR becomes the DR.
• The router with the highest router ID becomes the new BDR.
12. Which two statements describe the use of OSPF DR/BDR elections? (Choose two.)
• Elections are always optional.
• Elections are required in all WAN networks.
• Elections are required in point-to-point networks.
• Elections are required in broadcast multiaccess networks.
• Elections are sometimes required in NBMA networks.
13.

Refer to the exhibit. As part of an OSPF network, R1 and R2 are trying to become adjacent neighbors. Although it appears that the two systems are communicating, neither of the routing tables include OSPF routes received from its neighbor. What could be responsible for this situation?
• R1 and R2 are not on the same subnet.
• The Process IDs on each router do not match.
• The timer intervals on the routers do not match.
• The value set for the Transmit Delay time on both routers is too low.
14.

Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the value 128 shown in bold?
• It is the OSPF cost metric.
• It is the OSPF administrative distance.
• It is the value assigned by the Dijkstra algorithm that designates the distance in hops to the network.
• It is the value assigned to an interface that is used by the DUAL algorithm to determine the metric.
15.

Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the configuration commands added on router B?
• allows router A to form an adjacency with router B
• provides a stable OSPF router ID on router B
• provides a method of testing router traffic
• creates the OSPF adjacency table on router B
16.

Refer to the exhibit. The command ip route 10.16.1.64 255.255.255.252 s0/0/0 is entered into the router. Why does network 10.16.1.64/30 appear in the routing table in addition to network 10.16.1.64/27?
• The router views 10.16.1.64/30 and 10.16.1.64/27 as two different networks.
• The static route is used as a backup route for packets destined for 10.16.1.64/27.
• The AD for static routes is lower than the AD for OSPF routes.
• The static route metric is lower than the OSPF metric for the 10.16.1.64/27 network.
17. What is the primary difference between link-state protocols and distance vector protocols with regard to route calculation?
• Distance vector protocols take existing routes from their neighbors and add to them. Link-state protocols independently calculate full routes.
• Link-state protocols calculate and pass full routing tables to all routers in their associated areas, and distance vector protocols do not.
• When determining invalid routes, link-state protocols use split horizon for all route computations. Distance vector protocols use reverse poisoning.
• Distance vector protocols require more CPU and RAM for route calculations than link-state protocols require.
18. What range of networks are advertised in the OSPF updates by the command Router1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0?
• 192.168.0.0/24 through 192.168.0.15/24
• 192.168.0.0/24 through 192.168.15.0/24
• 192.168.15.0/24 through 192.168.31.0/24
• 192.168.15.0/24 through 192.168.255.0/24
• 192.168.16.0/24 through 192.168.255.0/24
19.

Refer to the exhibit. When establishing adjacency relationships, which IP address would router A use to send hello packets to router B?
• 10.11.0.1
• 10.11.0.2
• 10.11.0.255
• 224.0.0.5
• 255.255.255.255
20.

Refer to the exhibit. Which router will be elected the DR and which will become the BDR?
• R1 will be DR and R2 will be BDR.
• R1 will be DR and R3 will be BDR.
• R2 will be DR and R1 will be BDR.
• R2 will be DR and R3 will be BDR.
• R3 will be DR and R2 will be BDR.
• R3 will be DR and R1 will be BDR.
21. When compared to a distance vector routing protocol, what is a benefit of the hierarchical design approach that is used in large OSPF networks?
• simpler configuration
• reduction of router processing requirements
• isolation of network instability
• less complex network planning
22. What are two advantages of using a link-state routing protocol instead of a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two.)
• The topology database eliminates the need for a routing table.
• Frequent periodic updates are sent to minimize the number of incorrect routes in the topological database.
• Routers have direct knowledge of all links in the network and how they are connected.
• After the initial LSA flooding, routers generally require less bandwidth to communicate changes in a topology.
• A link-state routing protocol requires less router processor power.
23. If a network has converged, what is true about the link-state database held by each router in the same OSPF area?
• Each router has a link-state database containing the same status information.
• Each router has a different link-state database depending on its position within the network.
• The link-state database is stored in a designated router and is accessed by each router in the area as needed.
• The link-state database in each router only contains information about adjacent routers and the status of their links.
24.

Refer to the exhibit. RTRC was recently configured and is not sending the proper OSPF routes to RTRB, as shown in the RTRB routing table. Based on the RTRC configuration, what is most likely the problem?
• RTRC interfaces are administratively shut down.
• The OSPF process ID for RTRC does not match the process ID used on RTRB.
• The interface addresses on RTRC overlap with other addresses in the network.
• The OSPF routing configuration on RTRC has a missing or incorrect network statement.
CCNA Discovery 3 Module 5 Exam Answers Version 4.0
1. What three statements are true about routers that are configured for EIGRP? (Choose three.)
• They can support multiple routed protocols
• They can support only link-state protocols.
• They send their entire routing tables to neighboring routers.
• They send partial routing updates in response to topology changes.
• They send routing updates to all other routers in the network.
• They use hello packets to inform neighboring routers of their status.
2. Given the following commands:
Router(config)# router rip
Router(config-router)# network 192.31.7.0
What three conclusions can be determined based on the commands used on the router? (Choose three.)
• A link-state routing protocol is used.
• A distance vector routing protocol is used.
• Routing updates broadcast every 30 seconds.
• Routing updates broadcast every 90 seconds.
• Hop count is the only metric used for route selection.
• Bandwidth, load, delay, and reliability are metrics used for route selection.
3. What is indicated when an EIGRP route is in the passive state?
• The route has the highest path cost of all routes to that destination network.
• The route must be confirmed by neighboring routers before it is put in the active state.
• The route is a feasible successor and will be used if the active route fails.
• There is no activity on the route to that network.
• The route is viable and can be used to forward traffic.
4. What two problems may occur if the EIGRP default bandwidth for a serial link is higher than the actual bandwidth? (Choose two.)
• Routing updates will arrive too quickly for receiving routers to process.
• The port IP address will be rejected by the routing protocol.
• Suboptimal paths will be selected.
• The port protocol will return to the HDLC default.
• VLSM support will be disabled.
• Network convergence may be affected.
5. What is the default administrative distance for EIGRP internal routes?
• 70
• 90
• 100
• 110
• 120
• 255
6. A network administrator issues the command show ip route and sees this line of output:
192.168.3.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:05, Serial0/0
What two pieces of information can be obtained from the output? (Choose two.)
• RIP is the routing protocol configured.
• This is a static route to network 192.168.3.0.
• The metric for this route is 2.
• The next periodic update is in 5 seconds.
• The autonomous system number is 120.
7.

Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the EIGRP authentication configuration?
• RTA and RTB will accept updates from each other.
• RTA and RTB will not accept updates from each other because key 1 on RTB does not match RTA.
• RTA and RTB will not accept updates from each other because the key chain names do not match.
• The ip authentication mode AS does not match the locally configured AS.
8. Which Layer 4 protocol does EIGRP use to provide reliability for the transmission of routing information?
• DUAL
• IP
• PDM
• RTP
• TCP
• UDP
9.

Refer to the exhibit. Routers RTR-1 and RTR-3 are completely configured. The administrator needs to configure the routing protocol on router RTR-2 so that communication occurs throughout the network. Which group of commands will successfully configure EIGRP on RTR-2?
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.4 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.128 0.0.0.192 no-summary
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.192 0.0.0.192 area 0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.4 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.128 0.0.0.192
10. What prevents RIPv1 updates from being correctly advertised?
• an increase in network load
• the use of variable length subnet masks
• the use of multiple Layer 3 networks on the same router
• a variation in connection speeds on the links to a destination
• a mismatch between the configured bandwidth and the actual bandwidth of a link
11. What does a router that is running RIP use to determine the best path to take when forwarding data?
• the host portion of the network address
• the speed of network convergence
• the calculated metric for the destination network
• the number of broadcasts occurring on an interface
• the number of errors occurring on an interface
12. What is the purpose of the network command when RIP is being configured as the routing protocol?
• It identifies the networks connected to the neighboring router.
• It restricts networks from being used for static routes.
• It identifies all of the destination networks that the router is allowed to install in its routing table.
• It identifies the directly connected networks that will be included in the RIP routing updates.
13. How do EIGRP routers establish and maintain neighbor relationships?
• by exchanging neighbor tables with directly attached routers
• by comparing known routes to information received in updates
• by exchanging hello packets with neighboring routers
• by dynamically learning new routes from neighbors
• by exchanging routing tables with directly attached routers
14.

Refer to the exhibit. Routers A and B have EIGRP configured and automatic summarization has been disabled on both routers. Which router command will summarize the attached routes?
• ip area-range eigrp 1 192.168.10.80 255.255.255.224
• ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192
• ip summary-address 192.168.10.80 0.0.0.31
• ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63
• ip area-range eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.224
15. How often does RIPv2 send routing table updates, by default?
• every 30 seconds
• every 45 seconds
• every 60 seconds
• every 90 seconds
16.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a routing problem. When the show ip route command is entered on RTR-1, only the serial link between RTR-2 and RTR-3 has been learned from the RIP routing protocol. What are two issues? (Choose two.)
• RIPv1 is a classful routing protocol.
• RIPv1 does not support subnetting.
• The Ethernet networks on RTR-2 and RTR-3 were not entered correctly in the network statements on these routers.
• RIPv1 does not support VLSM.
• RIPv1 is a classless routing protocol.
17. What two statements are correct regarding EIGRP authentication? (Choose two.)
• EIGRP authentication uses the MD5 algorithm.
• EIGRP authentication uses a pre-shared key.
• EIGRP authentication requires that both routers have the same key chain name.
• EIGRP authentication uses varying levels of WEP to encrypt data exchanged between routers.
• EIGRP authentication can be configured on one router and updates from this router are protected; whereas a neighbor router can be without the authentication configuration and its updates are unprotected.
18. When should EIGRP automatic summarization be turned off?
• when a router has not discovered a neighbor within three minutes
• when a router has more than three active interfaces
• when a network contains discontiguous network addresses
• when a router has less than five active interfaces
• when a network addressing scheme uses VLSM
19. What is the maximum number of hops that RIP will attempt before it considers the destination unreachable?
• 14 hops
• 15 hops
• 16 hops
• 17 hops
20. What two statements are true regarding EIGRP tables? (Choose two.)
• A feasible successor route can be found in the topology table.
• A successor route can only be found in the routing table.
• The topology table shows whether a route is in the passive or active state.
• The routing table shows the amount of time elapsed since a router adjacency was formed.
• The neighbor table shows all adjacent Cisco devices.
• Administrative distance is shown as a column in the neighbor table.
21.

Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the output from the show ip protocols command?
• RIPv2 is configured on this router.
• Auto summarization has been disabled.
• The next routing update is due in 17 seconds.
• 192.168.16.1 is the address configured on the local router
• They can support multiple routed protocols
• They can support only link-state protocols.
• They send their entire routing tables to neighboring routers.
• They send partial routing updates in response to topology changes.
• They send routing updates to all other routers in the network.
• They use hello packets to inform neighboring routers of their status.
2. Given the following commands:
Router(config)# router rip
Router(config-router)# network 192.31.7.0
What three conclusions can be determined based on the commands used on the router? (Choose three.)
• A link-state routing protocol is used.
• A distance vector routing protocol is used.
• Routing updates broadcast every 30 seconds.
• Routing updates broadcast every 90 seconds.
• Hop count is the only metric used for route selection.
• Bandwidth, load, delay, and reliability are metrics used for route selection.
3. What is indicated when an EIGRP route is in the passive state?
• The route has the highest path cost of all routes to that destination network.
• The route must be confirmed by neighboring routers before it is put in the active state.
• The route is a feasible successor and will be used if the active route fails.
• There is no activity on the route to that network.
• The route is viable and can be used to forward traffic.
4. What two problems may occur if the EIGRP default bandwidth for a serial link is higher than the actual bandwidth? (Choose two.)
• Routing updates will arrive too quickly for receiving routers to process.
• The port IP address will be rejected by the routing protocol.
• Suboptimal paths will be selected.
• The port protocol will return to the HDLC default.
• VLSM support will be disabled.
• Network convergence may be affected.
5. What is the default administrative distance for EIGRP internal routes?
• 70
• 90
• 100
• 110
• 120
• 255
6. A network administrator issues the command show ip route and sees this line of output:
192.168.3.0/24 [120/2] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:05, Serial0/0
What two pieces of information can be obtained from the output? (Choose two.)
• RIP is the routing protocol configured.
• This is a static route to network 192.168.3.0.
• The metric for this route is 2.
• The next periodic update is in 5 seconds.
• The autonomous system number is 120.
7.

Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the EIGRP authentication configuration?
• RTA and RTB will accept updates from each other.
• RTA and RTB will not accept updates from each other because key 1 on RTB does not match RTA.
• RTA and RTB will not accept updates from each other because the key chain names do not match.
• The ip authentication mode AS does not match the locally configured AS.
8. Which Layer 4 protocol does EIGRP use to provide reliability for the transmission of routing information?
• DUAL
• IP
• PDM
• RTP
• TCP
• UDP
9.

Refer to the exhibit. Routers RTR-1 and RTR-3 are completely configured. The administrator needs to configure the routing protocol on router RTR-2 so that communication occurs throughout the network. Which group of commands will successfully configure EIGRP on RTR-2?
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.4 0.0.0.3 no-summary
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.128 0.0.0.192 no-summary
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.192 0.0.0.192 area 0
• RTR-2(config)# router eigrp 1
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.18.76.0 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.4 0.0.0.3
RTR-2(config-router)# network 198.198.76.128 0.0.0.192
10. What prevents RIPv1 updates from being correctly advertised?
• an increase in network load
• the use of variable length subnet masks
• the use of multiple Layer 3 networks on the same router
• a variation in connection speeds on the links to a destination
• a mismatch between the configured bandwidth and the actual bandwidth of a link
11. What does a router that is running RIP use to determine the best path to take when forwarding data?
• the host portion of the network address
• the speed of network convergence
• the calculated metric for the destination network
• the number of broadcasts occurring on an interface
• the number of errors occurring on an interface
12. What is the purpose of the network command when RIP is being configured as the routing protocol?
• It identifies the networks connected to the neighboring router.
• It restricts networks from being used for static routes.
• It identifies all of the destination networks that the router is allowed to install in its routing table.
• It identifies the directly connected networks that will be included in the RIP routing updates.
13. How do EIGRP routers establish and maintain neighbor relationships?
• by exchanging neighbor tables with directly attached routers
• by comparing known routes to information received in updates
• by exchanging hello packets with neighboring routers
• by dynamically learning new routes from neighbors
• by exchanging routing tables with directly attached routers
14.

Refer to the exhibit. Routers A and B have EIGRP configured and automatic summarization has been disabled on both routers. Which router command will summarize the attached routes?
• ip area-range eigrp 1 192.168.10.80 255.255.255.224
• ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192
• ip summary-address 192.168.10.80 0.0.0.31
• ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63
• ip area-range eigrp 1 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.224
15. How often does RIPv2 send routing table updates, by default?
• every 30 seconds
• every 45 seconds
• every 60 seconds
• every 90 seconds
16.

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a routing problem. When the show ip route command is entered on RTR-1, only the serial link between RTR-2 and RTR-3 has been learned from the RIP routing protocol. What are two issues? (Choose two.)
• RIPv1 is a classful routing protocol.
• RIPv1 does not support subnetting.
• The Ethernet networks on RTR-2 and RTR-3 were not entered correctly in the network statements on these routers.
• RIPv1 does not support VLSM.
• RIPv1 is a classless routing protocol.
17. What two statements are correct regarding EIGRP authentication? (Choose two.)
• EIGRP authentication uses the MD5 algorithm.
• EIGRP authentication uses a pre-shared key.
• EIGRP authentication requires that both routers have the same key chain name.
• EIGRP authentication uses varying levels of WEP to encrypt data exchanged between routers.
• EIGRP authentication can be configured on one router and updates from this router are protected; whereas a neighbor router can be without the authentication configuration and its updates are unprotected.
18. When should EIGRP automatic summarization be turned off?
• when a router has not discovered a neighbor within three minutes
• when a router has more than three active interfaces
• when a network contains discontiguous network addresses
• when a router has less than five active interfaces
• when a network addressing scheme uses VLSM
19. What is the maximum number of hops that RIP will attempt before it considers the destination unreachable?
• 14 hops
• 15 hops
• 16 hops
• 17 hops
20. What two statements are true regarding EIGRP tables? (Choose two.)
• A feasible successor route can be found in the topology table.
• A successor route can only be found in the routing table.
• The topology table shows whether a route is in the passive or active state.
• The routing table shows the amount of time elapsed since a router adjacency was formed.
• The neighbor table shows all adjacent Cisco devices.
• Administrative distance is shown as a column in the neighbor table.
21.

Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about the output from the show ip protocols command?
• RIPv2 is configured on this router.
• Auto summarization has been disabled.
• The next routing update is due in 17 seconds.
• 192.168.16.1 is the address configured on the local router
Kamis, 02 Desember 2010
punya neneng gi
Lab 3.4.3 Part B: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
Step 1: Connect the equipment
Step 2: Perform basic configurations on the router
Step 3: Configure VLAN trunking on the router
Step 4: .Configure Switch 1
Are all other switch ports in VLAN 1?
Which switch ports are in VLAN 10?
Which switch ports are in VLAN 20?
Issue the command show vlan.
What difference is noticed between the two commands show vlan brief and show vlan?
Step 5: Configure VLAN trunking on Switch 1
Which interfaces on Switch 1 are in trunk mode?
Which VLANs are allowed and active in the management domain?
Step 6: Configure VTP on Switch 1
Step 7: Configure Switch 2
Step 8: Configure VLAN trunking on Switch 2
Step 9: Configure VTP on Switch 2
Switch2(config)#vtp mode client
From Switch 2, verify that all VLANs have been propagated across the domain by issuing the command show vtp status.
What is the VTP version used on Switch 2?
What is the maximum VLANs supported locally?
What VTP operating mode is used on Switch 2?
What is the VTP domain name?
How did Switch 2 learn the domain name and VLAN information?
Step 10: Verify connectivity
The router and switches should be able to ping the interfaces of the other devices.
a. From each device, issue a ping to all interfaces.
Are the router pings successful?
b. From Switch 1, ping to all other devices.
Are Switch 1 pings successful?
From Switch 2, ping to all other devices.
Are Switch 2 pings successful? __________ If the ping is not successful, verify the connections and configurations again. Check to ensure that all cables are correct and that connections are seated. Check the router and switch configurations.
Step 11: Reflection
a. Why would VLANs be configured in a network?
b. Why would a VLAN benefit from trunking?
c. Why should VTP be used?
d. Which device provides connectivity between different VLANs?
e. What are some benefits of VLANs?
lab 3.4.3 punya neneng
Lab 3.4.3 Part A: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
Step 1: Connect the equipment
Step 2: Perform basic configurations on the router
Step 3: Configure Fast Ethernet connections for each VLAN on the router
Step 4: Configure Switch 1
Step 5: Configure Switch 2
Step 6: Configure Switch 3
Step 7: Configure Host 1
Step 8: Configure Host 2
Step 9: Configure Host 3
Step 10: Configure the server
Step 11: Verify connectivity
The router should be able to ping the interfaces of the other devices.
a. From the router, issue a ping to Host 1.
Is the ping successful?
b. From the router, issue a ping to Host 2.
Is the ping successful?
c. From the router, issue a ping to Host 3.
Is the ping successful?
d. From the router, issue a ping to the server.
Is the ping successful?
Host 1 should be able to ping all other devices.
a. From Host 1, ping Host 2.
Is the ping successful?
b. From Host 1, ping the server.
Is the ping successful?
Why can Host 1 ping the server?
c. From the server, ping Host 1.
Is the ping successful?
d. From Switch 3, issue the command show spanning-tree.
Which ports are being used on Switch 3?
What is the role of each of these ports?
Which switch is acting as the root?
What is the protocol that allows VLANs to communicate without switching loops?
Step 12: Reflection
a. Why does this topology not scale well?
b. Why would a VLAN benefit from trunking?
c. Which device provides connectivity between different VLANs?
Langganan:
Postingan (Atom)